Create & Manage Goals
Goals offer a straightforward and intuitive approach to defining and monitoring objectives. They serve as a unifying force, guiding the organization toward a shared purpose and enabling precise performance measurement and business evaluation. By prioritizing goals, teams and individuals are inspired to strive for excellence and achieve success.
Building Goals
First, review the annual goals and long-term problem list on the Business Vision Board. From there, answer the question: "What are the top 3 to 7 most important tasks to be done this quarter?"
Next, create each important goal by following these steps:
Step 1: Select the item
Choose the team that needs to set the goal. In the case of setting goals for the entire business, select the "Leadership team".
Click on the "Goal" button on the toolbar.
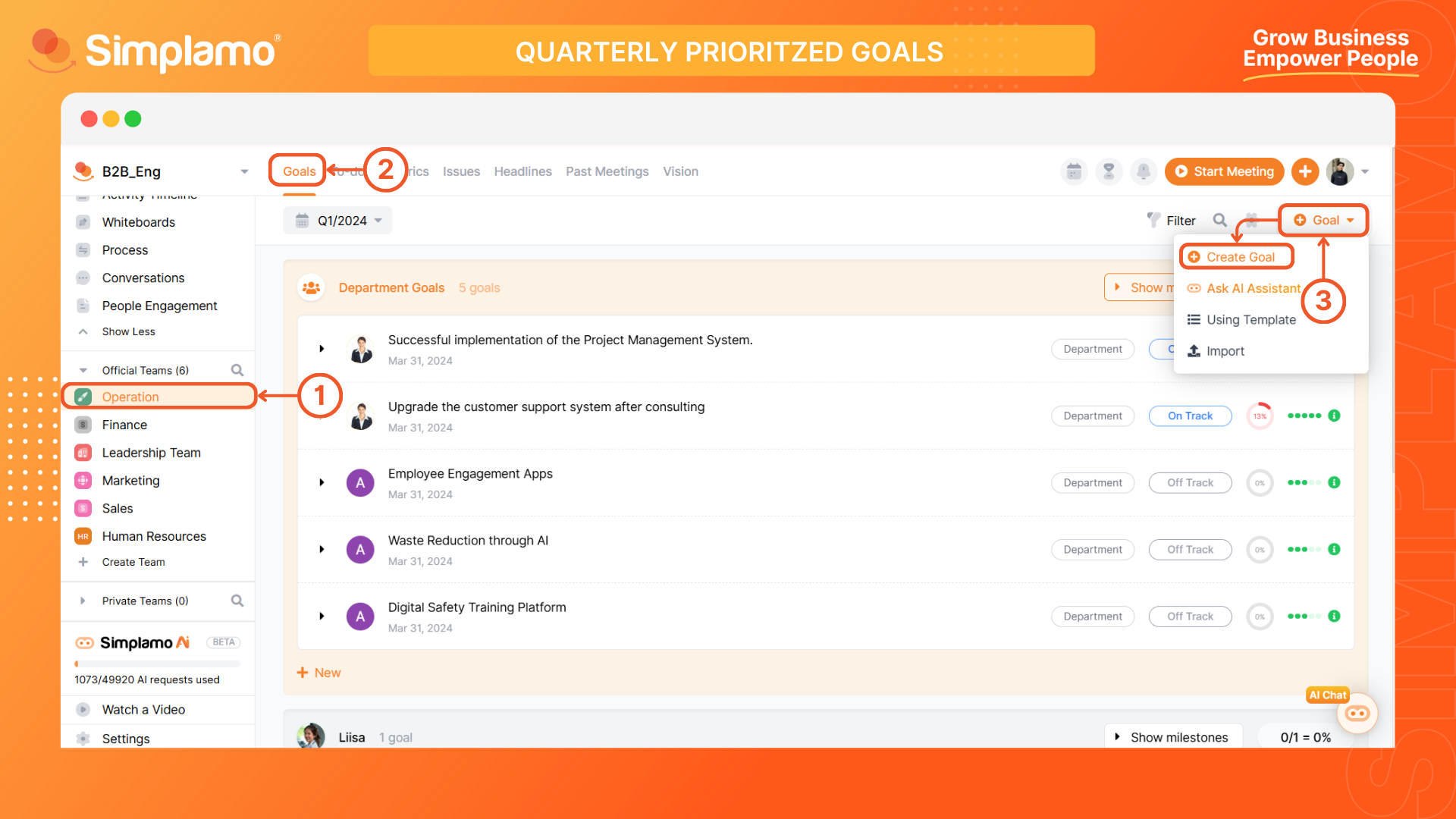
Step 2: Create a well-defined Goal
Select "Create Goal" to create a new goals and fill in the following information:
Define the Goal: Clearly articulate the "Title" and "Description," addressing
Choose the "Type" based on the company's hierarchy:
Why is this important?
Why is it urgent?
What is the outcome? This may include:
- Key results;
- Key actions;
- Key actions that need other department's support.
Set the Context: Choose the appropriate "Type" (Company, Department, or Individual) and "Session."
Select the appropriate "Goal Owner" based on the responsibility chart.
If the Goal supports another Goal, you can choose which Goal it contributes to by clicking "Support for anotehr Goal" and select your bigger Goal.
Finally, click "Create".
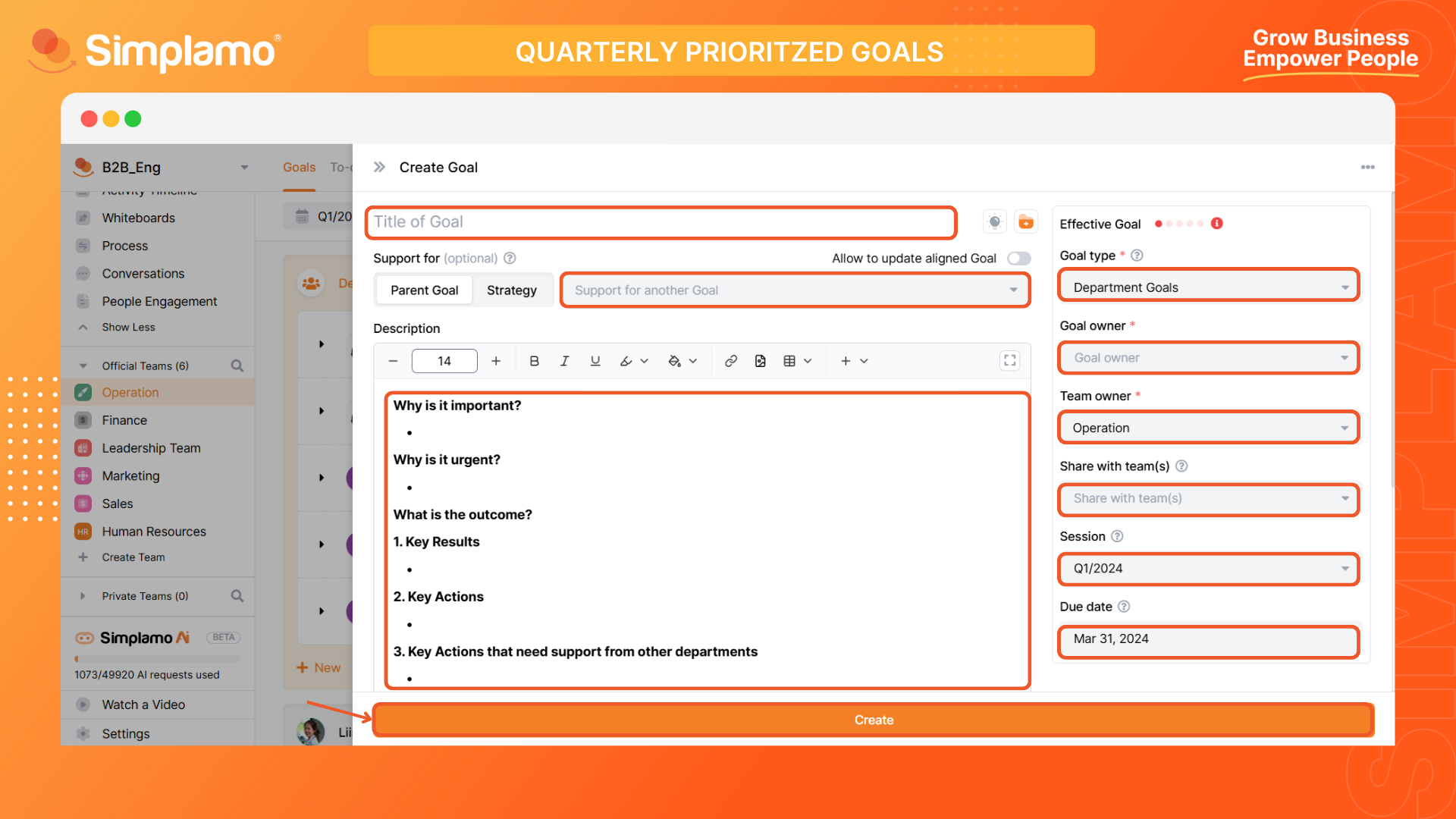
After creating the goals, pay attention to the “Effective Goal”. The quality criteria of a goal are important for measuring effectiveness, enhancing reliability, improving analysis and evaluation, as well as supporting goal management.
Tracking history
To view the history of goal on Simplamo, follow these steps:
In the goal editing interface, select the "Histories feature.
Histories on Simplamo records all relevant changes related to that goal, including:
- Name of the person who performed the action.
- Name of the action performed.
- Time of the action.
- Details of the changes made.
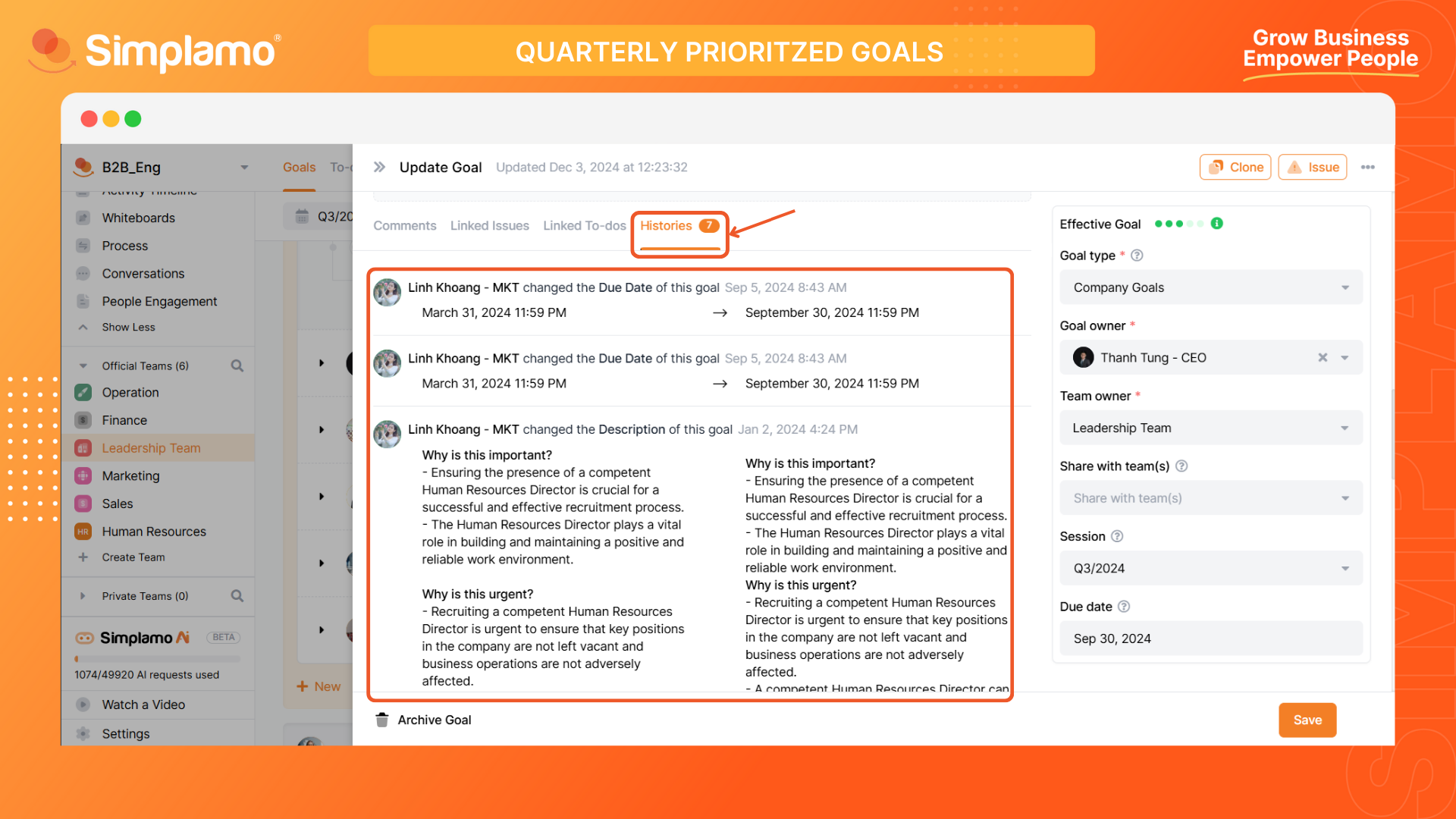
Reviewing the history of goal changes helps us understand the organization's or individual's evolution and development. It allows us to identify the right choices and mistakes that have been made, and adjust and optimize future goals.
Calculate Goal progress
Calculating the progress of a goal is essential for evaluating the implementation process. It helps determine the level of completion of tasks compared to the initial plan.
The progress states of a goal are:
- "On Track" is defined as between 1% and 99% completion.
- "Off Track" is defined as 0% completion.
- "Done" is defined as 100% completion.
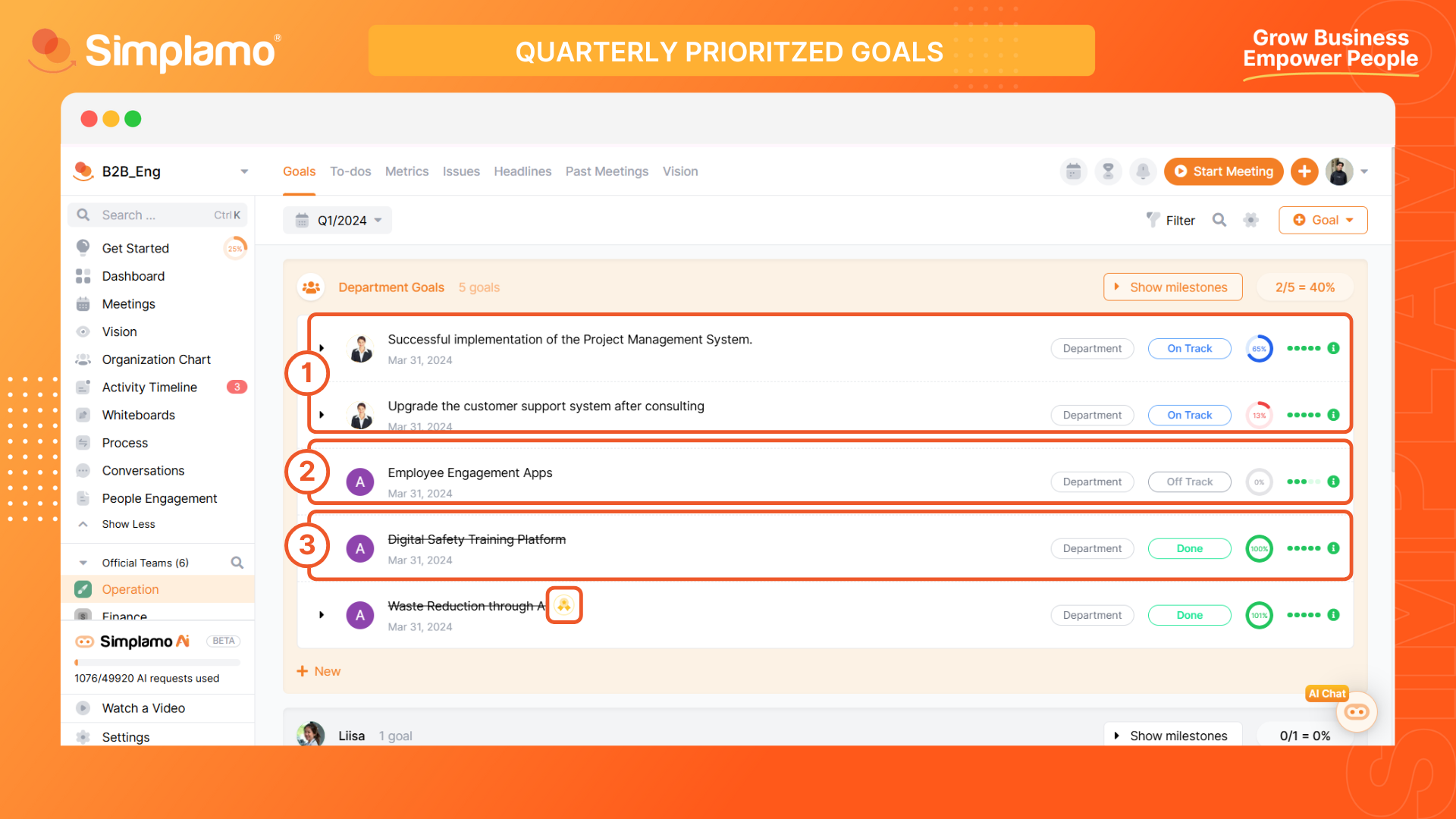
However, in cases where goals exceed the expected progress, Simplamo indicates this by displaying a "Medal" icon on the progress milestone column.
Leveraging Goal Status Alerts
Goal status alerts notify specific conditions, changes, or issues related to a particular goal. They help monitor and evaluate performance, automate and support decision-making, provide alerts and preventions, and ensure efficient operations and goal achievement.
The alert types based on the goal status are:
- Normal goal: These are goals that are within the execution plan and have not encountered any issues affecting progress. The system displays the goal in black. (1)
- Approaching deadline: These are goals that are close to the completion date but have not achieved sufficient progress or are facing obstacles during execution. The system displays the goal in yellow and provides a notification deadline of "7 days". (2)
- Overdue Goals: These are goaks that have reached or exceeded the completion date compared to the initial timeline. In this case, the system alerts by displaying the goals in red and shows the number of days overdue. (3)
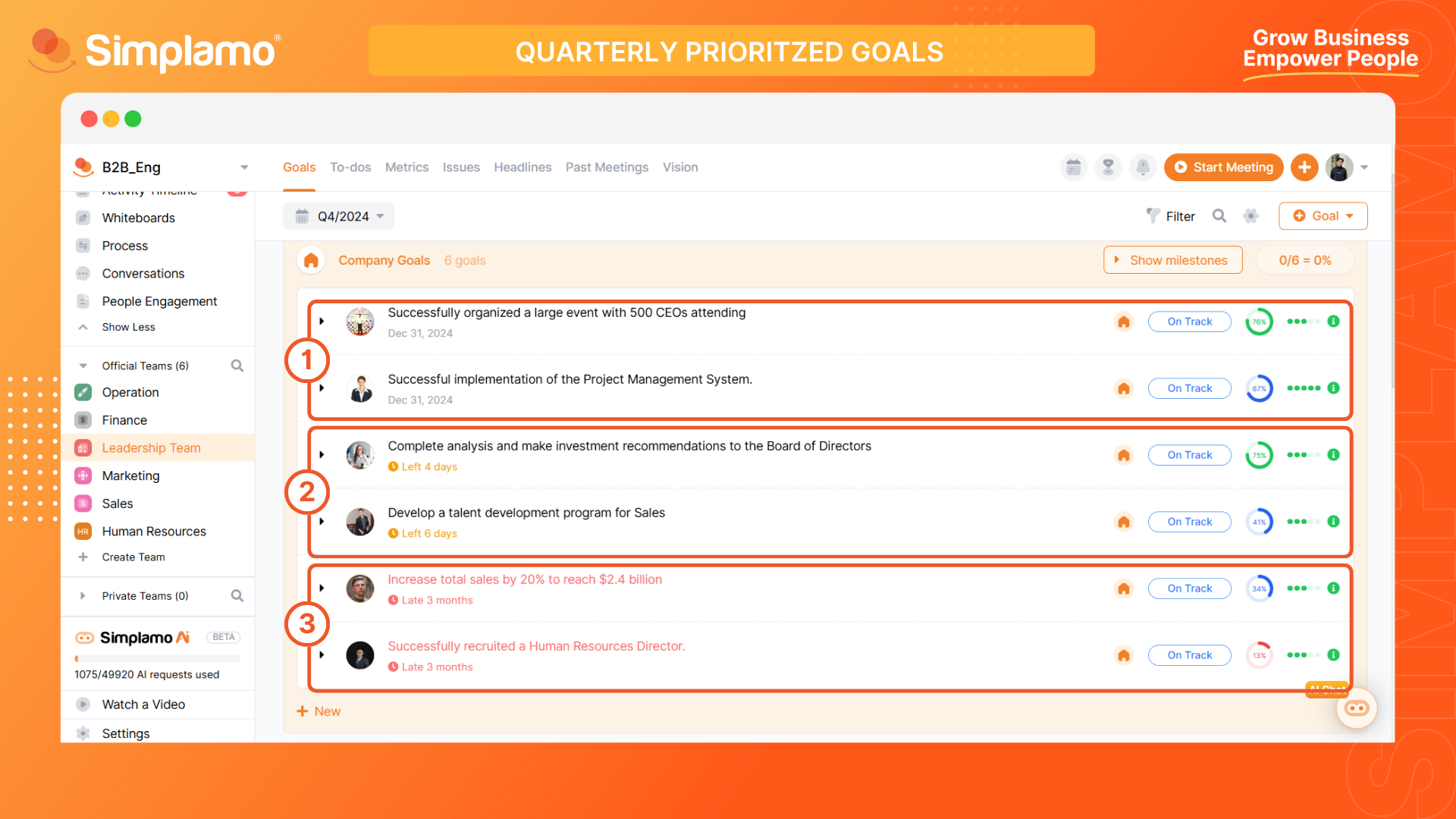
Note: For goals in the Approaching deadline or Overdue goal alert status, pay more attention and take necessary actions to ensure timely completion and collectively achieve the common objectives.